Showing posts with label KS2. Show all posts
Showing posts with label KS2. Show all posts
Thursday 4 May 2017
Year 6 Teachers, You've Got This! Your 5-Step Game Plan for SATs Week 2017
The latest in my series of blog posts for Third Space Learning focuses on SATs week itself. The focus is on teacher and pupil wellbeing and provides 5 steps to take to ensure year 6 teachers and pupils aren't too frazzled by the end of it.
So, the time has come. SATs week 2017 is upon us. On Monday morning, after months (hopefully years) of preparation, the nation's Year 6 children will sit down to the first of 2017's Key Stage 2 National Assessments.
Year 6 teachers across the land will be pacing halls and classrooms, catching glimpses of questions and hoping beyond hope that the primary school children in their classes will do their very best.
And I assume you're probably one of those teachers, or a supportive Head or SLT member.
You'll be feeling a heady mix of excitement and nervousness while anticipating the children’s chance to show off all they've learned. You might also be wondering what on earth the test-writers have come up with this time.
Click here to read on over at the Third Space Learning blog: http://thirdspacelearning.com/blog/2017/year-6-teachers-you-ve-got-this-your-5-step-game-plan-for-2017-ks2-sats
Sunday 2 April 2017
On the TES Blog: The 9 Essential Components of a KS2 Reading Scheme
After the shock results of the key stage 2 reading test last year, there is barely a primary school in the country that hasn't prioritised reading this year. There are many creative ways of encouraging not only a love of reading, but a high level of competence in the subject. You'll have your own, of course, but here’s a reminder of some of the basics that a good reading scheme can’t do without.
To read the 9 essential components head over to the TES blog:
To read the 9 essential components head over to the TES blog:
Monday 20 March 2017
On the TES Blog: Why Every Primary Should Be Using Bar Modelling – And Six Steps To Make It A Success
As a primary maths coordinator, it's been difficult to escape the lure of bar modelling: it's in every new publication, on all the maths blogs and at every coordinator's meeting. And so, when the time was right for my school, I succumbed.
Bar modelling, for the uninitiated, is not a method of calculation. Instead, it is a way of representing problems pictorially: from simple addition, through to finding percentages of amounts, all the way to complex multi-step problems involving ratio and proportion. Bar models can be used to pictorially represent arithmetic problems, as well as reasoning problems written with a context.
For a worked example of bar modelling and 6 steps to ensure introducing bar modelling is successful, read on at the TES blog:
https://www.tes.com/news/school-news/breaking-views/why-every-primary-should-be-using-bar-modelling
Bar modelling, for the uninitiated, is not a method of calculation. Instead, it is a way of representing problems pictorially: from simple addition, through to finding percentages of amounts, all the way to complex multi-step problems involving ratio and proportion. Bar models can be used to pictorially represent arithmetic problems, as well as reasoning problems written with a context.
For a worked example of bar modelling and 6 steps to ensure introducing bar modelling is successful, read on at the TES blog:
https://www.tes.com/news/school-news/breaking-views/why-every-primary-should-be-using-bar-modelling
Labels:
bar modelling,
KS1,
KS2,
mathematics,
Maths,
TES
Monday 13 March 2017
Book Review: 'The Night Spinner' by Abi Elphinstone
Ask a child what 'The Night Spinner' by Abi Elphinstone is about and they will speak of magic and monsters, adventure and action. But those are just plot features. Beneath all that, this is a book about far more.
In actual fact, this book is about loyalty, kindness, bravery, resilience - all those things we're attempting to teach our children through well-intentioned school display boards and PSHCE lessons. Where these attempts might not have long-term impact, a book like this, in the right hands, really could.
Aimed at Key Stage Two children, this rip-roaring adventure, where dull moments are banished, is the perfect vehicle for many-a lesson on those personality traits that we all agree are essential for our children to possess. As an adult, it's difficult to see where the reality of the story ends and metaphor begins: one of the book's main villains is a dead ringer for depression as she steadily drains the lead character, Molly, of all hope, leaving her feeling increasingly unable to go on with her quest. Throughout the book Molly, aided by a colourful array of characters, learns how better to deal with her feelings of self-doubt and becomes a case study in how to overcome adversity through perseverance. There is so much for children to learn about themselves as the thrilling story unfolds.
It's becoming increasingly popular for a female protagonist to be associated with action and adventure stories but Abi Elphinstone's trilogy is a welcome addition to the growing canon of books fronted by strong female leads. The fact that Molly Pecksniff - who doesn't flinch at jumping from a bridge onto a moving train with her wildcat - is a girl, certainly does not make this a book for girls. Whilst it is important that girls have such a positive role model, its also crucial that boys are presented with a character who really challenges gender stereotypes. Books like this have the power to change minds and shape thinking.
For all of this, 'The Night Spinner' and its two preceding volumes thoroughly deserve a prominent place on the shelves of our libraries and schools. Not that they will stay on the shelf for long!
In actual fact, this book is about loyalty, kindness, bravery, resilience - all those things we're attempting to teach our children through well-intentioned school display boards and PSHCE lessons. Where these attempts might not have long-term impact, a book like this, in the right hands, really could.
Aimed at Key Stage Two children, this rip-roaring adventure, where dull moments are banished, is the perfect vehicle for many-a lesson on those personality traits that we all agree are essential for our children to possess. As an adult, it's difficult to see where the reality of the story ends and metaphor begins: one of the book's main villains is a dead ringer for depression as she steadily drains the lead character, Molly, of all hope, leaving her feeling increasingly unable to go on with her quest. Throughout the book Molly, aided by a colourful array of characters, learns how better to deal with her feelings of self-doubt and becomes a case study in how to overcome adversity through perseverance. There is so much for children to learn about themselves as the thrilling story unfolds.
It's becoming increasingly popular for a female protagonist to be associated with action and adventure stories but Abi Elphinstone's trilogy is a welcome addition to the growing canon of books fronted by strong female leads. The fact that Molly Pecksniff - who doesn't flinch at jumping from a bridge onto a moving train with her wildcat - is a girl, certainly does not make this a book for girls. Whilst it is important that girls have such a positive role model, its also crucial that boys are presented with a character who really challenges gender stereotypes. Books like this have the power to change minds and shape thinking.
For all of this, 'The Night Spinner' and its two preceding volumes thoroughly deserve a prominent place on the shelves of our libraries and schools. Not that they will stay on the shelf for long!
Labels:
Book review,
books,
KS2,
reading,
reading for enjoyment
Wednesday 8 March 2017
Using Simple Bar Modelling Techniques To Solve Multi-Step SATs Problems
Bar Modelling is taking the primary maths world by storm. The 2014 curriculum appears, despite initial unhappiness, to be achieving a shift in the way maths is taught. Its three main aims of reasoning, problem solving and fluency have encouraged teachers to seek further ways to encourage conceptual understanding, rather than just teaching tricks or rules. So teachers have looked towards the countries who apparently churn out mastery-level mathematicians by the thousands for inspiration - that or some savvy publishers have decided to capitalise on the desire of teachers to teach the 'why' rather than the 'how'.
Click here to read more about bar modelling and the solution I came up with: https://thirdspacelearning.com/blog/2017/using-simple-bar-modelling-techniques-to-solve-multi-step-sats-problems
If you would like Aidan to work with you on developing maths at your school, please visit his website at https://www.aidansevers.com/services and get in touch via the contact details that can be found there.
Friday 10 February 2017
The Unexplainable Joy Of Comparing Books
Regular readers of this blog will know of the journey I've been on with reading. And now, having a good solid year of reading behind me, I'm really reaping the benefits. Of course, each book I read is a benefit in itself, but now I'm beginning to experience particular moments of awe and wonder. I know exactly what causes these moments but as yet am undecided on why they occur. I can't quite put my finger on what is so joyous about what essentially is this boring-sounding lesson objective: to make comparisons between texts.
A few years ago, every KS2 test had that part at the end where children were required to make comparisons between the texts they'd read during the test. The last of the current interim objectives for reading states that children should make comparisons within and across books although the KS2 reading test framework only asks that children should make comparisons within the text (and last year's test didn't test this at all). I recently wrote about pairing non-fiction texts with fiction texts but as far as I know teachers always paired fiction texts with other fiction texts - this is common practice.
I recently read the excellent 'The Goldfish Boy' by Lisa Thompson and I was struck, not by similarities (it's a highly original concept) but by the links I naturally made to other texts as I read. I was told of children trying to solve a mystery which occurs on a single street during the summer and was reminded of Michael Frayn's 'Spies' (a novel for adults and one of the best books I read last year). I read of a boy who lives with the guilt of feeling responsible for a younger brother's death (not a spoiler as this is revealed early in the book) and instantly recalled Patrick Ness' genre-defying 'More Than This' (and was also caused to reflect on the links between this and the latest series of 'Sherlock'). I made more overarching links to current favourite with teachers, 'Wonder' by R.J. Palacio, as both books deal well with the treatment of those who live with medical conditions.
Whilst reading 'Hitler's Canary' by Sandi Toksvig with my class I read 'The Boy in the Striped Pyjamas' by John Boyne with my book club (Friday lunchtime, read and discuss, read two more chapters before next week). Initially the links to be made were so strong that we all commented on how we kept forgetting which book it was we were reading: both set during World War Two, both a first person account told from the perspective of a young boy (Bruno or Bamse), the first chapters in both even mention the boys dressing up as ringmasters and performing plays! The links as we read became deeper: they each provide a different view of the Holocaust, with each book deepening the children's understanding of the other.
The next fiction text I will link to 'Hitler's Canary' will be a picture book: 'The Whispering Town' by Jennifer Elvgren and Fabio Santomauro. It's another account of how the majority of Denmark's Jews were smuggled out of the country to safety during World War Two; the Danish people working together to resist the Nazis. I'm hoping it will give the children the opportunity to engage with historical events in a different way. I'm no expert on picture books (seek out people like Mat Tobin and Simon Smith for people who really know their stuff) but I believe they harbour the potential to engage children at a deep and meaningful level within their few pages.
Deborah Wiles said, "Telling stories with visuals is an ancient art. We've been drawing pictures on cave walls for centuries. It's like what they say about the perfect picture book. The art and the text stand alone, but together, they create something even better. Kids who need to can grab onto those graphic elements and find their way into the story." I'm hoping these visuals will further spark the imaginations of the year 6 children and that they will feel that thrill of finding two stories that link. One of my favourite authors, Philip Reeve, said, "Even tiny children looking at a picture book are using their imaginations, gleaning clues from the images to understand what is happening, and perhaps using the throwaway details which the illustrator includes to add their own elements to the story." Just imagine the potential impact a series of linking texts, including picture books, could have on a child's imagination and understanding.
This blog post, unlike others of mine, is more of a statement of intent than anything. I've experienced that unexplainable excitement of making links between texts I've read and I want the children I teach to feel it too. I intend to be more intentional about is, seeking out and providing them with a rich tapestry of high quality fiction texts, many of them short to ensure breadth, to expand their mental library. Many of the children I teach have not been brought up on picture books and bedtime stories as I was - I feel it is my duty, and my privilege, to continue to share the joys of reading with them, with the hope that this will create a life-long love of books.
So, a couple of questions remain to be asked: when have you experienced that strange elation of making links between two or more books? Which fiction books do you use as paired texts in class? Perhaps you can even answer that which eludes me: why is it such a good feeling when I make a link between two books? I'd love to hear from you in the comments section below!
Monday 6 February 2017
Book Review: 'The Goldfish Boy' by Lisa Thompson
 Lisa Thompson cleverly intertwines a truly intriguing mystery story with an entertaining study of how people respond differently to loss. Whilst older primary-aged children will be gripped by the plot, they'll also be receiving a masterclass in empathy.
Lisa Thompson cleverly intertwines a truly intriguing mystery story with an entertaining study of how people respond differently to loss. Whilst older primary-aged children will be gripped by the plot, they'll also be receiving a masterclass in empathy.As with any good crime novel there are a plethora of characters, each very different, and each with their own emotional issues. There's Matthew, the main protagonist, with OCD; Jake the bully with chronic exzema and allergies; and Melody who seems to be obsessed by graveyards and death. The story takes place almost exclusively in one street during one summer so as well as the aforementioned children, there are a whole host of adult characters too, again, all very different. Someone is responsible for the disappearance of a toddler - but who? As Matthew investigates, hampered by his worsening OCD, the reader discovers more about each of the street's residents.
This would be a 5 star addition to any classroom - the work that could be done on inference and empathy through this book could be invaluable to how a child views the different people they meet in life. The concept that everyone has potentially hidden reasons for how they behave is an important one for children to grasp - it's the basis for being non-judgmental and kind to others. By studying the varying characters as more information is revealed, children will begin to infer the reasons as to why the characters behave as they do. In doing this, important lessons could be learned about how to treat others who might appear to be different.
The fact that carrying out such studies would further involve the children in the plot is testament to the author's skill; the more the reader engages in the emotional side of the book, the more they will enter into detective mode as they attempt to solve this exciting whodunit.
Using 'The Goldfish Boy' as a class novel would also provide perfect opportunities for children to discuss and explore their own emotions and feelings - the book providing a safe and neutral foundation for children to consider their own response to the information and events in the story.
Now excuse me whilst I go and beg budget holders for a class set of these... I'll ask the English leader AND our PSHCE coordinator as this book falls solidly into both of their remits.
Sunday 29 January 2017
Why your Maths interventions for KS2 SATs should not start in Year 6
When a primary school receives good Key Stage 2 SATs results, the whole school celebrates, and rightly so: all teachers in all year groups will have contributed to the success of each child who reaches Year 6 and sits those tests.
However, it is not uncommon for Year 6 teachers to feel a pressure that teachers in other year groups don't. When results aren't so good it is more likely for the teaching and learning in that last year of primary, as opposed to any other, to be called into question - I know, I've been there myself. And with such pressure it's not surprising that in Year 6 we can descend into last-minute panic of revision classes, interventions and extra Maths and English time, often to the detriment of other areas of learning. Ideally this wouldn't happen.
Click here to read the rest of the article over at the Third Space Learning blog.
However, it is not uncommon for Year 6 teachers to feel a pressure that teachers in other year groups don't. When results aren't so good it is more likely for the teaching and learning in that last year of primary, as opposed to any other, to be called into question - I know, I've been there myself. And with such pressure it's not surprising that in Year 6 we can descend into last-minute panic of revision classes, interventions and extra Maths and English time, often to the detriment of other areas of learning. Ideally this wouldn't happen.
Click here to read the rest of the article over at the Third Space Learning blog.
Monday 16 January 2017
Teaching Reading: Pairing Non-Fiction with Fiction
Having spent a term with year 6 on reading fiction (and answering questions based on fiction texts) data analysis pointed firmly towards non-fiction as being next on the agenda. Data analysis aside, the reading of non-fiction texts is one of the key ways in which we learn throughout life; as the outgoing POTUS said: "Reading makes all other learning possible". In addition to this, as I have explored in previous blog posts, having a greater knowledge base makes us better readers of fiction and although reading fiction is one way to experience and learn new ideas, non-fiction is arguably better for this purpose.
Still wanting to read a class novel (the reasons for my desire to do this are probably obvious and would take up an entire blog post for themselves) I realised now was the time to put into practice one of my key takeaways from 'Reading Reconsidered': the concept of embedding non-fiction and pairing texts.
In chapter 3 of 'Reading Reconsidered' the authors describe how shorter non-fiction texts chosen to run alongside a class novel fall into two main categories:
Inside the Bull's-Eye: contains "content necessary to support basic understanding of the primary [main] text" (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123)
Outside the Bull's-Eye: causes "students to look at the primary [main] text in a new and unexpected or more rigorous way"(Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123)
I would absolutely recommend that any teacher interested in teaching reading effectively read 'Reading Reconsidered' - the chapter on reading non-fiction is full of insights guaranteed to improve some aspect of practice. Focusing only on the Inside the Bull's-Eye category of text, here a just a few of those insights, the ones most relevant to this blog post:
"When students start from a base of knowledge, their inferences allow them to engage with the text with much greater depth - to learn from what they read as efficiently as possible. They're more attentive, both to the emotions of the characters and to the factual information presented in the fictional text." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123)
"When texts are paired, the absorption rate of both texts goes up." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123) The book also describes how children are more likely to understand a non-fiction text if they can relate its content to characters from a novel who they felt connected to - this particularly when the fiction text is begun to be read before introducing some of the non-fiction texts.
"...we typically choose [non-fiction] texts assuming that we are helping our students fill in knowledge gaps... but this results in non-fiction that constantly appears out of context..." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 125)
"Embedding, pairing non-fiction with related fiction, brings both to life." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 125)
So with this in mind I set about looking for paired texts to go with our current class novel 'Hitler's Canary' by Sandi Toksvig. The book is set during World War Two in Denmark and is all about the Danish underground resistance. It explore many themes such as antisemitism, homophobia and good and bad. As such, there are not a lot of books in our library with readily available texts to use as secondary texts so I began to prepare texts based on internet sources:
The main characters in the book are a family involved in theatre - there are constant references to theatre throughout the text (even the chapters are called, for example, Act 1 Scene 3) so my first paired non-fiction text was simply a list of theatre vocabulary - already, after reading just a few chapters, the learning from reading this has been invaluable.
The children in my class had not previously studied WW2 so it was important for them to have some context early on. Whilst we reading the second chapter we also read a fairly simple text, which included a world map, about the countries involved in the war; it also mentioned briefly the causes of the war.
The book fairly quickly throws up the idea of persecution, particularly antisemitic persecution. In passing pogroms are mentioned. Pogroms are not usually touched upon in primary schools however I saw it as a way into the whole concept of antisemitism. Rather than skim over the mention of pogroms, perhaps with a brief definition, I decided to prepare a linked text about them. It was full of challenging vocabulary (which the session focused on as well as information retrieval) but the children are already linking this level of persecution with every mention of a Jewish character in the story, helping them to understand the gravity of the situation some of the characters are facing.
Continuing on the theme of antisemitism and persecution I decided to preempt the part of the story when Jews begin to be taken away by the Nazis. I wanted, as mentioned previously, children to understand and anticipate how the Jewish characters (and their friends) would be feeling about the events in the story. For this I chose a non-fiction with a certain amount of narrative: the life story of Zigi Shipper, a holocaust survivor. As well as the narrative provided in the text, there is lots of simply communicated background information about the Nazis and their death camps.
All the resources referred to, along with the 'Reading Role'-linked comprehension activities that children completed alongside the secondary non-fiction texts are available to download here at the TES Resources site. This resource will continue to grow as we read more of 'Hitler's Canary'.
The challenge of this approach will be continuing to find a variety relevant texts - the temptation will be to provide an endless stream of 'non-chronological reports' rather than a mix of newspaper articles, advertisements, information leaflets, diary entries, letters and so on. Hopefully, with careful selection (and creation), I will be able to provide the children with a range of non-fiction text that increase their understanding of the events in 'Hitler's Canary' at the same time as bolstering their knowledge of World War Two and their understanding of issues such as racism and tolerance. As their knowledge and understanding grows, it will be interesting to see if their inferences do become more accurate - they are already engaging with the novel at a deeper level than a previous group of children who were not provided with the paired non-fiction text.
Still wanting to read a class novel (the reasons for my desire to do this are probably obvious and would take up an entire blog post for themselves) I realised now was the time to put into practice one of my key takeaways from 'Reading Reconsidered': the concept of embedding non-fiction and pairing texts.
In chapter 3 of 'Reading Reconsidered' the authors describe how shorter non-fiction texts chosen to run alongside a class novel fall into two main categories:
Inside the Bull's-Eye: contains "content necessary to support basic understanding of the primary [main] text" (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123)
Outside the Bull's-Eye: causes "students to look at the primary [main] text in a new and unexpected or more rigorous way"(Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123)
I would absolutely recommend that any teacher interested in teaching reading effectively read 'Reading Reconsidered' - the chapter on reading non-fiction is full of insights guaranteed to improve some aspect of practice. Focusing only on the Inside the Bull's-Eye category of text, here a just a few of those insights, the ones most relevant to this blog post:
"When students start from a base of knowledge, their inferences allow them to engage with the text with much greater depth - to learn from what they read as efficiently as possible. They're more attentive, both to the emotions of the characters and to the factual information presented in the fictional text." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123)
"When texts are paired, the absorption rate of both texts goes up." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 123) The book also describes how children are more likely to understand a non-fiction text if they can relate its content to characters from a novel who they felt connected to - this particularly when the fiction text is begun to be read before introducing some of the non-fiction texts.
"...we typically choose [non-fiction] texts assuming that we are helping our students fill in knowledge gaps... but this results in non-fiction that constantly appears out of context..." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 125)
"Embedding, pairing non-fiction with related fiction, brings both to life." (Lemov, Driggs & Woolway, page 125)
So with this in mind I set about looking for paired texts to go with our current class novel 'Hitler's Canary' by Sandi Toksvig. The book is set during World War Two in Denmark and is all about the Danish underground resistance. It explore many themes such as antisemitism, homophobia and good and bad. As such, there are not a lot of books in our library with readily available texts to use as secondary texts so I began to prepare texts based on internet sources:
The main characters in the book are a family involved in theatre - there are constant references to theatre throughout the text (even the chapters are called, for example, Act 1 Scene 3) so my first paired non-fiction text was simply a list of theatre vocabulary - already, after reading just a few chapters, the learning from reading this has been invaluable.
The children in my class had not previously studied WW2 so it was important for them to have some context early on. Whilst we reading the second chapter we also read a fairly simple text, which included a world map, about the countries involved in the war; it also mentioned briefly the causes of the war.
The book fairly quickly throws up the idea of persecution, particularly antisemitic persecution. In passing pogroms are mentioned. Pogroms are not usually touched upon in primary schools however I saw it as a way into the whole concept of antisemitism. Rather than skim over the mention of pogroms, perhaps with a brief definition, I decided to prepare a linked text about them. It was full of challenging vocabulary (which the session focused on as well as information retrieval) but the children are already linking this level of persecution with every mention of a Jewish character in the story, helping them to understand the gravity of the situation some of the characters are facing.
Continuing on the theme of antisemitism and persecution I decided to preempt the part of the story when Jews begin to be taken away by the Nazis. I wanted, as mentioned previously, children to understand and anticipate how the Jewish characters (and their friends) would be feeling about the events in the story. For this I chose a non-fiction with a certain amount of narrative: the life story of Zigi Shipper, a holocaust survivor. As well as the narrative provided in the text, there is lots of simply communicated background information about the Nazis and their death camps.
All the resources referred to, along with the 'Reading Role'-linked comprehension activities that children completed alongside the secondary non-fiction texts are available to download here at the TES Resources site. This resource will continue to grow as we read more of 'Hitler's Canary'.
The challenge of this approach will be continuing to find a variety relevant texts - the temptation will be to provide an endless stream of 'non-chronological reports' rather than a mix of newspaper articles, advertisements, information leaflets, diary entries, letters and so on. Hopefully, with careful selection (and creation), I will be able to provide the children with a range of non-fiction text that increase their understanding of the events in 'Hitler's Canary' at the same time as bolstering their knowledge of World War Two and their understanding of issues such as racism and tolerance. As their knowledge and understanding grows, it will be interesting to see if their inferences do become more accurate - they are already engaging with the novel at a deeper level than a previous group of children who were not provided with the paired non-fiction text.
If you would like Aidan to work with you on developing reading at your school, please visit his website at https://www.aidansevers.com/services and get in touch via the contact details that can be found there.
Labels:
#WeeklyBlogChallenge17,
comprehension,
inference,
KS2,
reading,
reading roles,
SATs
Friday 6 January 2017
Key Stage 2 SATs Results 2016 Explained: 15 Insights That Will Change How You Teach Year 6 Maths in 2017
 Given that I'm maths leader at my school you'd expect that my blog would contain more than just one post about maths, but it doesn't. Until now, that is. And even this one's not a full and proper post, only a link to a piece of work I've done for Third Space Learning.
Given that I'm maths leader at my school you'd expect that my blog would contain more than just one post about maths, but it doesn't. Until now, that is. And even this one's not a full and proper post, only a link to a piece of work I've done for Third Space Learning.I spent some time with the Question Level Analysis document produced by RAISE online, working out what the most difficult aspects of the KS2 tests were in 2016 so that hopefully we can all prepare our children well enough for the 2017 tests.
Click here to read the full in depth analysis: Key Stage 2 SATs Results 2016 Explained: 15 Insights That Will Change How You Teach Year 6 Maths in 2017
Labels:
#WeeklyBlogChallenge17,
arithmetic,
key stage 2 tests,
KS2,
mathematics,
Maths,
SATs,
Testing
Thursday 22 December 2016
UPDATED: Teaching Reading: A Simple Approach
In response to the 2016 KS2 Reading Test I've spent quite a bit of time researching and re-thinking my approach to teaching reading. This has resulted in the creation of a few resources which I've already blogged about. I have been asked a few times about the context in which I use these resources - this blog post will outline what a basic reading lesson might look like. Following the links throughout will lead you to more thorough information about the techniques and ideas mentioned.
Timetabling - my reading lessons happen on Wednesday, Thursday and Friday from 8:45 - 9:45. The children come in to a 'Do Now' which usually involves reading the day's chapter/passage/excerpt independently (more on this later). On those mornings I also teach writing-focused English for the following hour and then 1.5 hours of maths after break.
Whole-Class Reading - I do not have a 'traditional' carousel of activities. All children read and answer questions about the same text; research shows that children benefit from being exposed to higher level texts (when the teacher reads it aloud to them before they answer questions on it). Many of my reading lessons are based on a class novel which we read over a half term or a term; to facilitate this we have 'class sets' of many quality texts. Many people ask how the lower prior attainers can be catered for in these sessions - I've written more about that here. For more on the ideology behind whole-class reading please read Rhoda Wilson's blog post about it.
Lesson Sequence - During these sessions I ask the children to first read the chapter/excerpt independently, then I read the same passage aloud, then without discussion the children attempt to independently work through the questions giving written answers. Once the majority of children have done this we hold a whole-class discussion and I (or children who have written good answers) model best answers and children edit what they have written (in purple so as to distinguish their original answer from their edited answer). This sequence was inspired by Reading Reconsidered by Doug Lemov. This will usually be followed by a period of reading aloud the next part of the text (usually by me but I plan to begin to ask children to read aloud more often) which is often, but not always, accompanied by lots of discussion and modelling of my thought processes as a reader.
Reading For Pleasure - Many school plan elaborate initiatives in an attempt to entice children into reading with the hope that this will lead to them choosing to read for pleasure. My reading lessons always contain a time of just reading the class novel for enjoyment - books are the most powerful tool when it comes to getting children to love and enjoy reading. I've written more about it here in my blog post entitled 'On Why I'll Still Be Dressing Up For World Book Day And The Power Of Books'.
Comprehension Activities - I use the various question stem documents which are available to set my questions, and I colour-code each question and put the relevant Reading Roles symbol with them (see below for more on Reading Roles). Many of these comprehension activities will follow my Scaffolding Inference structure (see below) although I do teach other lessons which focus on the other cognitive domains. Examples of these activities can be found here. I have written a whole blog post entitled 'How To Write Good Comprehension Questions' which gives more insight into how I go about setting questions for reading lessons. In at least some lessons there is a focus on particular reading strategies, such as inference-making which I have written about here: Questions To Ask When Teaching Inference-Making.
Reading Roles - help children and staff understand the 8 cognitive domains. Each of the cognitive domains is colour-coded and has a symbol assigned - as mentioned, we use these colours and symbols when designing our comprehension activities. Reading Roles have been used by other teachers in other schools - some of them have written about it here.
Scaffolding Inference - this is something I've designed and developed based on research and findings from last year's SATs. Please see the quick reference guide which outlines this approach. I would say that this is the most effective thing I have done as it focuses on the reading test's three key areas: vocabulary, retrieval and inference. Not only can inference be scaffolded, other reading strategies can too: Scaffolding Structures For Reading Comprehension Skills.
Growing Background Knowledge - this isn't always easy to do as background knowledge can vary so much from child to child. What we do know is that our understanding of a text hinges greatly on what we already know - this might be a knowledge of vocabulary or just a more general knowledge. I have written about possible strategies to take when it comes to building children's background knowledge: 5 Ways To Make Texts With Unfamiliar Contexts More Accessible To Children; Attacking Children's Immunity To Imaginative Literature.
EAL reading activity structure - this is an activity (again, linked to the Reading Roles) which I have designed based on research on how to support EAL learners when accessing new texts.
Pairing non-fiction texts with fiction texts - this increases understanding of both the fiction text and the non-fiction text and has sparked some really deep conversations about moral, ethical and religious issues. I have also written about this for the TES: Why Every Primary School Needs To Embrace Non-Fiction.
We also use these resources in English lessons (with our Talk 4 Writing texts) and topic lessons - much of our work centres around texts so these activities help to ensure children comprehend the information.
The fruit of this approach is that in December over 50% of children in my group taking the 2016 KS2 Reading Test were working at or above average (according to the test's thresholds) after one term of year 6. This is a dramatic increase when compared to my results in last year's END of year results based on the same test.
If there is something you feel I've not covered, please ask and I will edit this to give a fuller picture of my approach. I'm not assuming it to be a silver bullet but am seeing good results after teaching in this way for a term.
Timetabling - my reading lessons happen on Wednesday, Thursday and Friday from 8:45 - 9:45. The children come in to a 'Do Now' which usually involves reading the day's chapter/passage/excerpt independently (more on this later). On those mornings I also teach writing-focused English for the following hour and then 1.5 hours of maths after break.
Whole-Class Reading - I do not have a 'traditional' carousel of activities. All children read and answer questions about the same text; research shows that children benefit from being exposed to higher level texts (when the teacher reads it aloud to them before they answer questions on it). Many of my reading lessons are based on a class novel which we read over a half term or a term; to facilitate this we have 'class sets' of many quality texts. Many people ask how the lower prior attainers can be catered for in these sessions - I've written more about that here. For more on the ideology behind whole-class reading please read Rhoda Wilson's blog post about it.
Lesson Sequence - During these sessions I ask the children to first read the chapter/excerpt independently, then I read the same passage aloud, then without discussion the children attempt to independently work through the questions giving written answers. Once the majority of children have done this we hold a whole-class discussion and I (or children who have written good answers) model best answers and children edit what they have written (in purple so as to distinguish their original answer from their edited answer). This sequence was inspired by Reading Reconsidered by Doug Lemov. This will usually be followed by a period of reading aloud the next part of the text (usually by me but I plan to begin to ask children to read aloud more often) which is often, but not always, accompanied by lots of discussion and modelling of my thought processes as a reader.
Reading For Pleasure - Many school plan elaborate initiatives in an attempt to entice children into reading with the hope that this will lead to them choosing to read for pleasure. My reading lessons always contain a time of just reading the class novel for enjoyment - books are the most powerful tool when it comes to getting children to love and enjoy reading. I've written more about it here in my blog post entitled 'On Why I'll Still Be Dressing Up For World Book Day And The Power Of Books'.
Comprehension Activities - I use the various question stem documents which are available to set my questions, and I colour-code each question and put the relevant Reading Roles symbol with them (see below for more on Reading Roles). Many of these comprehension activities will follow my Scaffolding Inference structure (see below) although I do teach other lessons which focus on the other cognitive domains. Examples of these activities can be found here. I have written a whole blog post entitled 'How To Write Good Comprehension Questions' which gives more insight into how I go about setting questions for reading lessons. In at least some lessons there is a focus on particular reading strategies, such as inference-making which I have written about here: Questions To Ask When Teaching Inference-Making.
Reading Roles - help children and staff understand the 8 cognitive domains. Each of the cognitive domains is colour-coded and has a symbol assigned - as mentioned, we use these colours and symbols when designing our comprehension activities. Reading Roles have been used by other teachers in other schools - some of them have written about it here.
Scaffolding Inference - this is something I've designed and developed based on research and findings from last year's SATs. Please see the quick reference guide which outlines this approach. I would say that this is the most effective thing I have done as it focuses on the reading test's three key areas: vocabulary, retrieval and inference. Not only can inference be scaffolded, other reading strategies can too: Scaffolding Structures For Reading Comprehension Skills.
Growing Background Knowledge - this isn't always easy to do as background knowledge can vary so much from child to child. What we do know is that our understanding of a text hinges greatly on what we already know - this might be a knowledge of vocabulary or just a more general knowledge. I have written about possible strategies to take when it comes to building children's background knowledge: 5 Ways To Make Texts With Unfamiliar Contexts More Accessible To Children; Attacking Children's Immunity To Imaginative Literature.
EAL reading activity structure - this is an activity (again, linked to the Reading Roles) which I have designed based on research on how to support EAL learners when accessing new texts.
Pairing non-fiction texts with fiction texts - this increases understanding of both the fiction text and the non-fiction text and has sparked some really deep conversations about moral, ethical and religious issues. I have also written about this for the TES: Why Every Primary School Needs To Embrace Non-Fiction.
We also use these resources in English lessons (with our Talk 4 Writing texts) and topic lessons - much of our work centres around texts so these activities help to ensure children comprehend the information.
The fruit of this approach is that in December over 50% of children in my group taking the 2016 KS2 Reading Test were working at or above average (according to the test's thresholds) after one term of year 6. This is a dramatic increase when compared to my results in last year's END of year results based on the same test.
If there is something you feel I've not covered, please ask and I will edit this to give a fuller picture of my approach. I'm not assuming it to be a silver bullet but am seeing good results after teaching in this way for a term.
If you would like Aidan to work with you on developing reading at your school, please visit his website at https://www.aidansevers.com/services and get in touch via the contact details that can be found there.
Click here to read about how following these approaches impacted on our SATs results.
Further reading about reading from my blog:
Being A Reading Teacher
Reading: 2 Things All Parents and Teachers Must Do
Reading: Attacking Children's Immunity To Imaginative Literature
Reading for Pleasure
Changing Hearts, Minds, Lives and the Future: Reading With Children For Empathy
The Best RE Lesson I Ever Taught (Spoiler: It Was A Reading Lesson)
The Unexplainable Joy of Comparing Books
The More-ness of Reading
The Power Of Books
Click here to read about how following these approaches impacted on our SATs results.
Further reading about reading from my blog:
Being A Reading Teacher
Reading: 2 Things All Parents and Teachers Must Do
Reading: Attacking Children's Immunity To Imaginative Literature
Reading for Pleasure
Changing Hearts, Minds, Lives and the Future: Reading With Children For Empathy
The Best RE Lesson I Ever Taught (Spoiler: It Was A Reading Lesson)
The Unexplainable Joy of Comparing Books
The More-ness of Reading
The Power Of Books
Labels:
comprehension,
KS2,
reading,
reading roles,
SATs
Thursday 1 December 2016
Reading Roles: Elements Of The Content Domain Made Memorable
A few years ago there were many resources available supporting children's understanding of the Assessment Focuses. Teachers found it beneficial to help children to identify the kinds of questions they were being asked about texts. The idea behind making children aware of the question type is that they might have a better idea of what the answer should look like in order to give better verbal and written answers.
With the recent introduction of the content domain (as set out in the English Reading Test Framework) and the upset caused by the difficulty of last year's KS2 reading test I set about reviving an idea that an old colleague of mine and I had a few years ago. Back then, we joked about conceiving it and setting up as consultants, peddling it around the local area but it wasn't even worth creating the resource as there were so many out there already that did the job just fine. Others out there are devising ways to help children understand the elements of the content domain however I believe the simple resource I have devised has some merits.
The concept of 'Reading Roles' is to assign a well-known job, role or profession to each of the domains. Most children will already understand what the jobs entail in real life and therefore will fairly immediately be able to gain an understanding of each element of the content domain. We have been trialing this for a number of weeks now and the children are already able to articulate what questions in each domain require of them. There is still work to be done - confidence in identifying question types consistently, but they now have the tool to do so.
Here are the 8 elements of the content domain and their assigned 'roles' (written for KS2):
This resource can be downloaded here, along with its KS1 counterpart and posters for both KS1 and KS2 containing one domain/role on each page.
As is obvious each domain is colour-coded and is assigned a simple symbol as a memory aid. We have used the colours and symbols to identify question types in the comprehension tasks we have set - the aim of this is to familiarise the children with the question types. Eventually we will remove the colours and symbols and focus more on question type identification. See here for examples of the comprehension tasks I've set in this way.
Click here for some testimonials from people who have used Reading Roles effectively in their school.
Again, as with the Scaffolding Inference technique, I'd love to hear from anyone who begins to use this. It'd be very interesting to see how this helps other children and in what ways it can be developed and used.
With thanks to Herts for Learning for the focus of each element of the content domain.
With the recent introduction of the content domain (as set out in the English Reading Test Framework) and the upset caused by the difficulty of last year's KS2 reading test I set about reviving an idea that an old colleague of mine and I had a few years ago. Back then, we joked about conceiving it and setting up as consultants, peddling it around the local area but it wasn't even worth creating the resource as there were so many out there already that did the job just fine. Others out there are devising ways to help children understand the elements of the content domain however I believe the simple resource I have devised has some merits.
The concept of 'Reading Roles' is to assign a well-known job, role or profession to each of the domains. Most children will already understand what the jobs entail in real life and therefore will fairly immediately be able to gain an understanding of each element of the content domain. We have been trialing this for a number of weeks now and the children are already able to articulate what questions in each domain require of them. There is still work to be done - confidence in identifying question types consistently, but they now have the tool to do so.
Here are the 8 elements of the content domain and their assigned 'roles' (written for KS2):
This resource can be downloaded here, along with its KS1 counterpart and posters for both KS1 and KS2 containing one domain/role on each page.
As is obvious each domain is colour-coded and is assigned a simple symbol as a memory aid. We have used the colours and symbols to identify question types in the comprehension tasks we have set - the aim of this is to familiarise the children with the question types. Eventually we will remove the colours and symbols and focus more on question type identification. See here for examples of the comprehension tasks I've set in this way.
Click here for some testimonials from people who have used Reading Roles effectively in their school.
Again, as with the Scaffolding Inference technique, I'd love to hear from anyone who begins to use this. It'd be very interesting to see how this helps other children and in what ways it can be developed and used.
With thanks to Herts for Learning for the focus of each element of the content domain.
Labels:
cognitive domains,
KS1,
ks1 sats,
KS2,
ks2 sats,
ks2 testing,
reading,
reading roles,
SATs,
SATs ks2
Wednesday 9 November 2016
Scaffolding Inference (Quick Reference Guide)
Inference skills in the new cognitive domains are summarised as:
2d: make inferences from the text / explain and justify inferences with evidence from the text
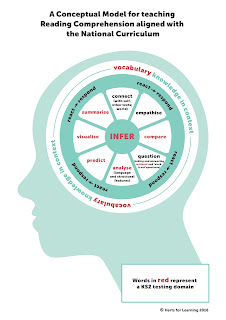
 Penny Slater's helpful article 'Reading Re-envisaged' explores the links between vocabulary knowledge and inference skills. Her conceptual model (pictured left) represents how inference skills rely on good knowledge and understanding of vocabulary. In her own words:
Penny Slater's helpful article 'Reading Re-envisaged' explores the links between vocabulary knowledge and inference skills. Her conceptual model (pictured left) represents how inference skills rely on good knowledge and understanding of vocabulary. In her own words:
"...the model signifies the importance of vocabulary knowledge. If we consider each circle to be a moat which the children must cross before they are able to access the skills within the innermost circles, then we see clearly that they will not get very far if they do not understand the meanings on the words on the page. This chimes with what teachers are finding in their classrooms: lack of knowledge of vocabulary is a complete blocker. You can’t make any inroads into comprehension without addressing this issue first."
So, another cognitive domain comes into play, one which children must be confident with if they are going to be able to make inferences:
2a: give / explain the meaning of words in context
This approach also explore the possibility that development of inference skills could be supported through the use of retrieval skills.
2b: retrieve and record information / identify key details from fiction and non-fiction
The Theory
The theory that I have been trialing is that inference skills can be taught by first studying the vocabulary used and then retrieving relevant information before going on to make inferences about a text. If inference is 'a conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning' then first a reader must be able to identify where the evidence is (retrieval) and before that the reader needs to understand the words used to present the evidence. In the model I propose (see right) the understanding of vocabulary is the foundation on which information retrieval is built, which in turn provides the support for making inferences.
The Practice
1. Decide on an inference question (2d); the question stems based on the 2016 KS2 reading test made available by Herts for Learning on their blog are really useful for this.
2. Begin to work backwards - work out where in the text the children need to go to locate useful evidence and ask a suitable retrieval question (2b).
3. Continue to work backwards - which words or phrases do the children need to understand in order to be able to understand the evidence then ask a careful vocabulary question (2a).
4. Once this process is complete (it may take a while at first), check that the 2a and 2b questions will adequately lead the children into answering the 2d question. If not, go back and tweak the questions.
For a more in-depth exploration of this technique, including examples of questions: http://thatboycanteach.blogspot.co.uk/2016/10/scaffolding-inference-trialling.html
Many of the examples from the blogpost are available for download here:
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/-11416437
2d: make inferences from the text / explain and justify inferences with evidence from the text
 Penny Slater's helpful article 'Reading Re-envisaged' explores the links between vocabulary knowledge and inference skills. Her conceptual model (pictured left) represents how inference skills rely on good knowledge and understanding of vocabulary. In her own words:
Penny Slater's helpful article 'Reading Re-envisaged' explores the links between vocabulary knowledge and inference skills. Her conceptual model (pictured left) represents how inference skills rely on good knowledge and understanding of vocabulary. In her own words: "...the model signifies the importance of vocabulary knowledge. If we consider each circle to be a moat which the children must cross before they are able to access the skills within the innermost circles, then we see clearly that they will not get very far if they do not understand the meanings on the words on the page. This chimes with what teachers are finding in their classrooms: lack of knowledge of vocabulary is a complete blocker. You can’t make any inroads into comprehension without addressing this issue first."
So, another cognitive domain comes into play, one which children must be confident with if they are going to be able to make inferences:
2a: give / explain the meaning of words in context
This approach also explore the possibility that development of inference skills could be supported through the use of retrieval skills.
2b: retrieve and record information / identify key details from fiction and non-fiction
The theory that I have been trialing is that inference skills can be taught by first studying the vocabulary used and then retrieving relevant information before going on to make inferences about a text. If inference is 'a conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning' then first a reader must be able to identify where the evidence is (retrieval) and before that the reader needs to understand the words used to present the evidence. In the model I propose (see right) the understanding of vocabulary is the foundation on which information retrieval is built, which in turn provides the support for making inferences.
The Practice
1. Decide on an inference question (2d); the question stems based on the 2016 KS2 reading test made available by Herts for Learning on their blog are really useful for this.
2. Begin to work backwards - work out where in the text the children need to go to locate useful evidence and ask a suitable retrieval question (2b).
3. Continue to work backwards - which words or phrases do the children need to understand in order to be able to understand the evidence then ask a careful vocabulary question (2a).
4. Once this process is complete (it may take a while at first), check that the 2a and 2b questions will adequately lead the children into answering the 2d question. If not, go back and tweak the questions.
For a more in-depth exploration of this technique, including examples of questions: http://thatboycanteach.blogspot.co.uk/2016/10/scaffolding-inference-trialling.html
Many of the examples from the blogpost are available for download here:
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/-11416437
Labels:
inference,
KS2,
reading,
reading for enjoyment,
reading roles,
SATs,
scaffolding inference,
teaching
Wednesday 5 October 2016
Scaffolding Inference: Trialling a Teaching Technique
If you are short of time but would like to get the gist of this technique, please see my Quick Reference Guide: http://thatboycanteach.blogspot.co.uk/2016/11/scaffolding-inference-quick-reference.html

With inference being the most-assessed skill in the Key Stage 2 reading tests it is no wonder that teachers spend a lot of time attempting to teach children how to infer meaning from texts, with varying degrees of success. It's the sort of skill that readers (by that I mean those who make a regular habit of reading, and enjoy it) possess without really learning. Because of this, it is a skill that is hard to teach; many teachers infer naturally so deconstructing how they do it in order to teach a process to children can be difficult.

With inference being the most-assessed skill in the Key Stage 2 reading tests it is no wonder that teachers spend a lot of time attempting to teach children how to infer meaning from texts, with varying degrees of success. It's the sort of skill that readers (by that I mean those who make a regular habit of reading, and enjoy it) possess without really learning. Because of this, it is a skill that is hard to teach; many teachers infer naturally so deconstructing how they do it in order to teach a process to children can be difficult.
In case you missed it, the reading test framework has rearranged reading skills into eight content domains. The fourth domain, the one we are concerned with here, is:
2d: make inferences from the text / explain and justify inferences with evidence from the text
Background Reading
The chapter in 'Reading Reconsidered' entitled 'Writing for Reading' (read an excerpt here) discusses the various structures a teacher might use within a reading session. The ideas presented widen the scope of how different task sequences can support the development of different skills. This made me think more carefully about how the teaching and learning sequence could build to help children to infer more successfully.
The chapter in 'Reading Reconsidered' entitled 'Writing for Reading' (read an excerpt here) discusses the various structures a teacher might use within a reading session. The ideas presented widen the scope of how different task sequences can support the development of different skills. This made me think more carefully about how the teaching and learning sequence could build to help children to infer more successfully.
Penny Slater's helpful article 'Reading Re-envisaged' explores the links between vocabulary knowledge and inference skills initiated the thinking that led to my development and trial of this method. Her conceptual model (pictured left) represents how inference skills rely on good knowledge and understanding of vocabulary. In her own words:
"...the model signifies the importance of vocabulary knowledge. If we consider each circle to be a moat which the children must cross before they are able to access the skills within the innermost circles, then we see clearly that they will not get very far if they do not understand the meanings on the words on the page. This chimes with what teachers are finding in their classrooms: lack of knowledge of vocabulary is a complete blocker. You can’t make any inroads into comprehension without addressing this issue first."
Anne Kispal's 'Effective Teaching of Inference Skills for Reading', in section 2.3 (page 26) goes into more detail on this and the document as a whole is an informative read. It has also been shown that 95%-98% of the vocabulary in a text needs to be understood in order to be able to derive a general meaning of the text (Schmitt, Jiang & Grabe, 2011).
So, another content domain comes into play, one which children must be confident with if they are going to be able to make inferences:
So, another content domain comes into play, one which children must be confident with if they are going to be able to make inferences:
2a: give / explain the meaning of words in context
I also had an inkling that development of inference skills could be supported through the use of retrieval skills.
2b: retrieve and record information / identify key details from fiction and non-fiction
Children usually find retrieval easier than inference, however it is worth noting that in the 2016 KS2 tests even some of the retrieval questions were difficult, often because of the vocabulary skills that are needed in order to retrieve information. There are plenty of places to learn about how to improve vocabulary skills, so I won't go into detail on that in this article, but I must stress that it is important that children are taught skills such as contextual and morphemic analysis before they attempt the process I suggest. Before my own trial I spent around 4 weeks focusing on teaching vocabulary skills, allowing the children plenty of time to practice.
The Theory
The theory that I have been trialing is that inference skills can be taught by first studying the vocabulary used and then retrieving relevant information before going on to make inferences about a text. If inference is 'a conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning' then first a reader must be able to identify where the evidence is (retrieval) and before that the reader needs to understand the words used to present the evidence. In the model I propose (see right) the understanding of vocabulary is the foundation on which information retrieval is built, which in turn provides the support for making inferences.
The Practice
In short:
Here's an example of a very scaffolded set of questions - the scaffold questions (questions 1, 2 and 3) make the answer to question 4 very obvious.
This one worked so successfully that I actually encouraged the children to further their answers for number 4 by explaining how the evidence showed that the children were unsure how to treat August - this was not initially required of them, and when compared to similar questions in the 2016 KS2 test, this would be classed as an inference (2d) question without the addition of an explanation. It also made me contemplate giving them the inference question to answer before the scaffold questions, as well as after, in order to compare the difference and the impact the scaffold questions have on the quality of answer.
Some more activity examples:
One more example:
What Next?
If this way of scaffolding inference questions works for the children in my class then I will begin to adapt it in order to support the development of skills outlined in the other content domains:
The trial of this technique for scaffolding inference is in its infancy. As such I will follow up this blog post with others including commentary on what I learn, further examples of questions and some more examples of children's work showing the impact.
I would also love to engage in discussion on this idea - please use the comments section to tell me where I am going wrong, to point me in the direction of relevant research or additional reading or to share your own examples if you decide to try it!
Click here to read a testimonial from one teacher who used the technique.
Click here to read about how this, and other changes made to the way we teach reading, impacted on our SATs results.
The theory that I have been trialing is that inference skills can be taught by first studying the vocabulary used and then retrieving relevant information before going on to make inferences about a text. If inference is 'a conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning' then first a reader must be able to identify where the evidence is (retrieval) and before that the reader needs to understand the words used to present the evidence. In the model I propose (see right) the understanding of vocabulary is the foundation on which information retrieval is built, which in turn provides the support for making inferences.
The Practice
In short:
- Decide on an inference question (2d); the question stems based on the 2016 KS2 reading test made available by Herts for Learning on their blog are really useful for this.
- Begin to work backwards - work out where in the text the children need to go to locate useful evidence and ask a suitable retrieval question (2b).
- Continue to work backwards - which words or phrases do the children need to understand in order to be able to understand the evidence then ask a careful vocabulary question (2a).
- Once this process is complete (it may take a while at first), check that the 2a and 2b questions will adequately lead the children into answering the 2d question. If not, go back and tweak the questions.
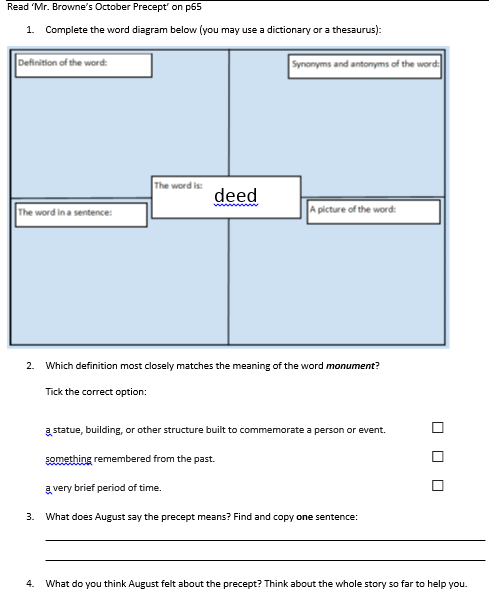
There are different ways in which the 2a and 2b questions might provide a scaffold for answering the 2b question. In order to explain this I will share some examples. All the examples are based on 'Wonder' by R.J. Palacio. I chose 'Wonder' as our first class novel because although it is fairly heavy in subject matter, it is easy-going with its vocabulary. I wanted to begin by supporting children's acquisition of vocabulary skills in a non-threatening manner before we started to read novels with more advanced language.
The first excerpt takes place in the chapter entitled 'The Summer Table' in which a girl named Summer joins August who is alone at a lunch table on his first day at school.
In the first example (pictured above ) the scaffolding structure can be seen clearly: question 1 is a 2a question, question 2 is a 2b question and question 3 is a 2d question. There is a very obvious grammar discussion to be had to surrounding common nouns and proper nouns - the children asked for clarification on this despite the words in question 1 not being capitalised. The discussion we had cleared up possible later misconceptions that Summer meant the table was only for people named Summer - a misconception which would have been at odds with the basic fact that August was also sitting at the table. I've noticed that test questions are often set about texts with potential misconceptions so I try to take opportunities to incorporate similar tricky bits in my teaching.
The second example is taken from the same chapter; the text follows directly the previous excerpt:
The second example does not lead the children directly to the answer for question 3 but it does provide background knowledge which should inform their own thoughts on the motivation for Summer's actions. In answering question 1 the children realised that there was a long list of names and by answering question 2 they began to get the sense that the quote in question 3 was true; they gained their own insight into why August says that most of the names weren't actually summer names. Questions 1 and 2 allowed the children to understand what Summer was doing (making a long list, bending the rule that only children with summer names could sit on the table) before they began to think about why she was doing it.
Question 3 actually also requires previous knowledge of the text - the children must have already grasped that August (a boy with facial birth defects) is sitting alone on his first ever day in school whilst children whisper about his looks in order to infer that Summer agrees that so many children can sit with them so that he finds more friends. The more perceptive children might also realise that Summer also wants him to have fun so that he forgets about his situation and so that he feels like all the other children. I was satisfied that our previous reading and dialogic discussion (thanks Mat Tobin for the terminology) meant that they understood the whole text well enough to approach this question.
It should also be noted that here there are two retrieval questions and no vocabulary-based question; the vocabulary they needed had been covered in the previous set of questions.
Here is an example of a child's work. This task was undertaken independently directly after completing the previous task (see above). The first task was completed independently prior to a whole-class discussion and then children edited their answers (with a purple pen) based on the discussion that was had. This example contains no edits - the child was able to answer question 3 successfully first time. It is worth noting that this child is one of the best readers in my class - for her the scaffold has had almost immediate impact. In further blog posts on this subject I will provide before and after evidence.
Here is an example of a child's work. This task was undertaken independently directly after completing the previous task (see above). The first task was completed independently prior to a whole-class discussion and then children edited their answers (with a purple pen) based on the discussion that was had. This example contains no edits - the child was able to answer question 3 successfully first time. It is worth noting that this child is one of the best readers in my class - for her the scaffold has had almost immediate impact. In further blog posts on this subject I will provide before and after evidence.
For the next examples I must give credit to Rhoda Wilson for her excellent 'Moving Beyond Comprehension Sheets' resource as I used it along with the Herts for Learning question stems to vary the question styles in these activities.
Here's an example of a very scaffolded set of questions - the scaffold questions (questions 1, 2 and 3) make the answer to question 4 very obvious.
This one worked so successfully that I actually encouraged the children to further their answers for number 4 by explaining how the evidence showed that the children were unsure how to treat August - this was not initially required of them, and when compared to similar questions in the 2016 KS2 test, this would be classed as an inference (2d) question without the addition of an explanation. It also made me contemplate giving them the inference question to answer before the scaffold questions, as well as after, in order to compare the difference and the impact the scaffold questions have on the quality of answer.
Some more activity examples:
Here is an example of child's work. This child entered year 6 in September assessed at a year 4 standard for reading. This method appears to have been very successful for him, even after only a few times working in this way.
One more example:
What Next?
If this way of scaffolding inference questions works for the children in my class then I will begin to adapt it in order to support the development of skills outlined in the other content domains:
2c; summarise main ideas from more than one paragraph
2e: predict what might happen from details stated and implied
2f: identify / explain how information / narrative content is related and contributes to meaning as a whole
2g: identify / explain how meaning is enhanced through choice of words and phrases
2h: make comparisons within the textIt will also be important to begin to remove the scaffolding - for some children sooner than others - in order to encourage children to use the skills independently; one question often raised against methods such as this is how will this approach help children when the structure is removed, for example, in the SATs reading test? And it's a good question. My hope is that it will provide them with a method for answering inference questions; a method which will be embedded in their way of working. If this technique is successful then children will naturally make inferences using their ability to understand the vocabulary (these skills will need to be taught in addition to this method of scaffolding questions) and their ability to locate and retrieve information from the text.
The trial of this technique for scaffolding inference is in its infancy. As such I will follow up this blog post with others including commentary on what I learn, further examples of questions and some more examples of children's work showing the impact.
I would also love to engage in discussion on this idea - please use the comments section to tell me where I am going wrong, to point me in the direction of relevant research or additional reading or to share your own examples if you decide to try it!
Click here to read a testimonial from one teacher who used the technique.
Click here to read about how this, and other changes made to the way we teach reading, impacted on our SATs results.
Labels:
inference,
KS1,
KS2,
reading,
reading roles,
SATs,
scaffolding inference
Saturday 28 May 2016
I Thought I'd Lose My Job.
This blog post is now available at: https://www.aidansevers.com/post/a-year-6-teacher-s-sats-memoir-i-thought-i-d-lost-my-job
Sunday 24 April 2016
A Year 6 Teacher's Vows
I do solemnly declare that I, your year 6 teacher, shall not pressurise you, my year 6 pupils, during the run up to the SATs. From this day forward, until lunchtime on May 12th, and indeed thereafter, I shall not subject you to emotional torture and shall protect you (to the best of my ability) from the ills of Key Stage 2 testing.
I promise that I will strive to keep you stimulated and engaged, even as together we learn the difference between coordinating and subordinating conjunctions. I will be a good teacher, for better, for worse, and I shall not continually mention that the SATs are coming up. Instead I will endeavour to prepare you for the rest of your lives until we are parted by the spring bank holiday, and eventually the six weeks holiday.
I pledge that I will respect, trust, help, and care for you, remembering that after all, you are fragile people with real emotions. I will persevere with you, in sickness and in health, not only to secure for you academic success but emotional wellbeing, social ability and general well-roundedness.
And when July comes, I promise to reassure you, in joy and in sorrow, that I, your year 6 teacher, believe that you, my year 6 pupils, really do have qualities that the test could not test. I will be your champion, reminding you that you have the capacity to succeed in a myriad of different ways as you express your own unique personalities and skill-sets. And as the last day of school rolls around, and we are rent asunder, I will wave you off, confident that your sanity and happiness remains intact as you look forward to blissful weeks of summer.
This is my solemn vow.
Sunday 21 February 2016
All Aboard!
In 'All In The Same Boat' I touched very briefly on today's subject matter and after a couple of conversations after yesterday's post it became clear that more needs to be said. Previously I wrote "Make sure your leadership are taking responsibility too - don't let them allow you to be alone in the boat" and I'd like to say a little more.
I am going to address this post to year 2 and year 6 teachers, but if you are a senior leader reading this, it is your responsibility to make sure that everything I suggest they do actually happens.
Most leaders will naturally want to be on board - it's their school and their data. Most leaders won't be leaving year 2 and year 6 teachers to hoist the mainsail themselves. Many leaders will now be adopting an 'all hands on deck' approach, but even the best captain needs to know from his crew what is happening in each area of the ship's life. He'll need the quartermaster to inform him when the ship is low on supplies, and he'll need the boatswain to tell him if such-and-such a part is in need of repair. Head teachers, and other members of SLT, will need feedback from teachers in order to understand what the needs and priorities are. And that's where this blog post comes in.
At the earliest possible opportunity, call a meeting with phase leaders (UKS2 and KS1), class teachers (Y2 and Y6), the head and any other SLT members. At the meeting discuss the new assessment arrangements (if you have not done so already) and its implications. If you have new thoughts and feelings after last week's revelations then it will be worth having another meeting anyway. It might be a good idea to take some assessment information with you so that you can identify the areas of greatest need. It'll also be good to approach it with some ideas already - if you go with only problems and no solutions the meeting will take longer, plus leaders always like to see a bit of initiative. Arm yourself with a list of questions you'd like to ask too. The meeting then needs to become a practical planning meeting with decisions made on what your school approach will be to this year's assessments. It's also worth considering as a team how you are going to keep a balanced curriculum instead of just doing maths and English (read this excellent blog post on the matter).
Even if you don't get to have a proper meeting, it'd be wise to ensure that the leadership of your school knows the course you are deciding to take with your year 2 or year 6 class. I would also involve them in any changes you're planning to make. Even when you begin to feel like you're pestering them, keep on asking for advice and informing them of your decisions.
The point of all this?
In short; make sure everyone is on board with everything that will end in assessment this year. Do everything you can do get the support that you need - even the best leaders need proactivity from their team.
Photo Credit: Eje Gustafsson via Compfight cc
I am going to address this post to year 2 and year 6 teachers, but if you are a senior leader reading this, it is your responsibility to make sure that everything I suggest they do actually happens.
Most leaders will naturally want to be on board - it's their school and their data. Most leaders won't be leaving year 2 and year 6 teachers to hoist the mainsail themselves. Many leaders will now be adopting an 'all hands on deck' approach, but even the best captain needs to know from his crew what is happening in each area of the ship's life. He'll need the quartermaster to inform him when the ship is low on supplies, and he'll need the boatswain to tell him if such-and-such a part is in need of repair. Head teachers, and other members of SLT, will need feedback from teachers in order to understand what the needs and priorities are. And that's where this blog post comes in.
At the earliest possible opportunity, call a meeting with phase leaders (UKS2 and KS1), class teachers (Y2 and Y6), the head and any other SLT members. At the meeting discuss the new assessment arrangements (if you have not done so already) and its implications. If you have new thoughts and feelings after last week's revelations then it will be worth having another meeting anyway. It might be a good idea to take some assessment information with you so that you can identify the areas of greatest need. It'll also be good to approach it with some ideas already - if you go with only problems and no solutions the meeting will take longer, plus leaders always like to see a bit of initiative. Arm yourself with a list of questions you'd like to ask too. The meeting then needs to become a practical planning meeting with decisions made on what your school approach will be to this year's assessments. It's also worth considering as a team how you are going to keep a balanced curriculum instead of just doing maths and English (read this excellent blog post on the matter).
Even if you don't get to have a proper meeting, it'd be wise to ensure that the leadership of your school knows the course you are deciding to take with your year 2 or year 6 class. I would also involve them in any changes you're planning to make. Even when you begin to feel like you're pestering them, keep on asking for advice and informing them of your decisions.
The point of all this?
- So that you're not alone in the boat at your school.
- So that you are supported.
- So that collective wisdom, and the wisdom that comes from experience, influences decisions.
- So that you have the chance to suggest that more manpower might be needed.
- So that when the data eventually comes in, it is data that represents a team effort.
- And so that no leader can make accusations of you, blaming poor results on you alone. This should not be about taking one for the team, but taking one AS a team.
In short; make sure everyone is on board with everything that will end in assessment this year. Do everything you can do get the support that you need - even the best leaders need proactivity from their team.
Photo Credit: Eje Gustafsson via Compfight cc
Saturday 20 February 2016
All In The Same Boat

Now that we've all experienced the cocktail of initial relief, mild anger and nervous hilarity that the DfE's announcements yesterday generated, it's time to think soberly and wisely about it. My 'DfE Tells Teachers They're All Very Naughty' was a crude response, yet it did seem to voice the opinion and feeling of many teachers upon hearing what Mr. Gibb and Ms. Morgan had to say (@theprimaryhead's post was much better). What we teachers, however, really need to focus on now is making sure that, for our students, the next few months are worthwhile.
The positives that came out of yesterday's communication from the department are that it appears schools will not be judged too harshly based on the outcomes of this year's assessment. Nick Gibb wrote this in his letter to the NAHT:
"I have also written to Her Majesty’s Chief Inspector asking that his inspectors take into account national performance and the contextual factors you have outlined when considering a school's performance on writing at Key Stage 2. All organisations holding schools to account should be aware of the changes being introduced in 2016 and will consider the impact of this in making any decisions about performance or intervention on the basis of 2016 data alone. This should give schools the confidence to engage fully with the vision of the new curriculum and to rise to the new standards."
He's actually right. We should have the confidence to go on teaching, even if he had never said this. Even if we know our RAISE online could go blue next year. Even if we know Ofsted will not look kindly on us. Because what we have to focus on is the children - we have a responsibility to them first and foremost. And in a sense it has always been this way in year 6: teachers have always had the role of gatekeeper, protecting the children from the pressure. Sadly, some teachers have never managed this, instead subjecting children to weeks and weeks of practise papers under exam conditions and taking every opportunity to brow-beat them with "It's only x amount of weeks until your SATs, you know?" Some teachers pass on the pressure they feel - and, at all costs, we must not do that.
In another communication from yesterday the DfE let us know that:
"As this is the first year of new accountability measures and new assessments, we will wait until tests have been taken to set minimum expectations for a school’s progress scores."
We must also remember this: the scores will be calculated based on the tests taken nationally and if everyone does poorly then the minimum expectation will be set lower. We're all in this together and if the DfE stick to what they've said this week then perhaps we shouldn't worry as much.
Although the DfE have tried to shy away from admitting that this has all been a bit shambolic,lines like this give it away: "Significant reforms such as these take time to get right and for the system to catch up." We're all in the same boat; teachers, school leaders, inspectors and government officials should all be chalking this year up to experience.
At the end of my first year teaching in year 6 I thought my world was going to come crashing down around me. Some children hadn't achieved as highly as I had hoped, despite acing many a past paper. There were certain issues when comparing the data to the previous year's data. I thought I was for the chop. I spent hours writing documents to defend each and every poor test score, compiling evidence to prove that my teacher judgments weren't way off the mark. I sat in front of the school leaders and even our school improvement partner to defend myself. It all lasted about a week, and then life went on. They asked me to teach in year 6 again and my current school employed me to teach in year 6 too: last year saw a ten percent rise in children achieving floor standards or above.
That year when it all went wrong is now long gone and forgotten, in fact it was all gone and forgotten after a few weeks. The school went on to get a 'Good' Ofsted inspection (with two ares being 'Outstanding') despite the data which I thought would end the world (in fact, there was barely any mention of the data).
And when 2017 rolls around 2016 will be gone and forgotten too. Whatever happens this year will not be career-defining for you. Realising that every year 2 and 6 teacher in the land is in the same position is key to having a more positive outlook on this matter. Knowing that when schools are compared, aside from the usual variations, there will be a national trend. That trend will not necessarily be a trend of 'underachievement' because I know that every year 2 and 6 teacher in the country will be working their socks off to ensure excellent progress and high achievement for all their children. Possibly the tests, and even the teacher assessment based on the interim objectives, will show that we are 'underachieving', but we will all be there together - maybe then the DfE will admit that their handling of the changes was clumsy. Maybe they won't. Whatever happens, it will all blow over and we will all move on.
In the meantime, steel yourself for Monday, plan and teach some exciting lessons and make sure the kids are learning and making progress. Don't foist the stress on to them; they're just kids. Make sure your leadership are taking responsibility too - don't let them allow you to be alone in the boat. Do the wise thing and make sure you teach them according to the curriculum and the interim objectives - do what you can with the short time we've got, but just remember that there are only so many hours in a day, week, half term. Maximise that time so that you can be confident your children will 'perform' to the best of their ability. And that is all you can ask for.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)