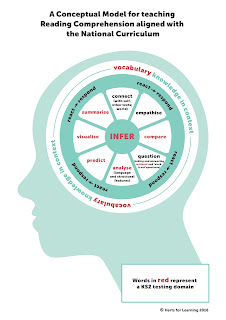
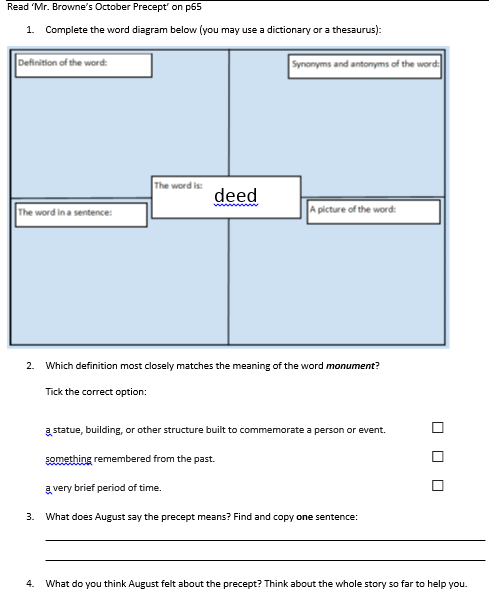
On 14th September, just as we were all getting settled into the new school year, the DfE published not one, but two documents of considerable importance: ‘Primary assessment in England: Government consultation response’ and the 2017/2018 ‘Teacher assessment frameworks at the end of KS2’. Both documents reveal changes that will no doubt affect our approach as teachers and leaders.
Whilst the most imminent and significant changes involve writing and reading, there are also some interesting developments in Maths.
Click here to read more: https://www.thirdspacelearning.com/blog/2017/9-changes-to-primary-maths-curriculum-and-assessment-slt-guide
The documents referred to throughout are these ones:
Primary Assessment Consultation Response: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/644871/Primary_assessment_consultation_response.pdf
Teacher Assessment Frameworks At The End of Key Stage 2: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/645021/2017_to_2018_teacher_assessment_frameworks_at_the_end_of_key_stage_2_PDFA.pdf
The documents referred to throughout are these ones:
Primary Assessment Consultation Response: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/644871/Primary_assessment_consultation_response.pdf
Teacher Assessment Frameworks At The End of Key Stage 2: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/645021/2017_to_2018_teacher_assessment_frameworks_at_the_end_of_key_stage_2_PDFA.pdf